Image
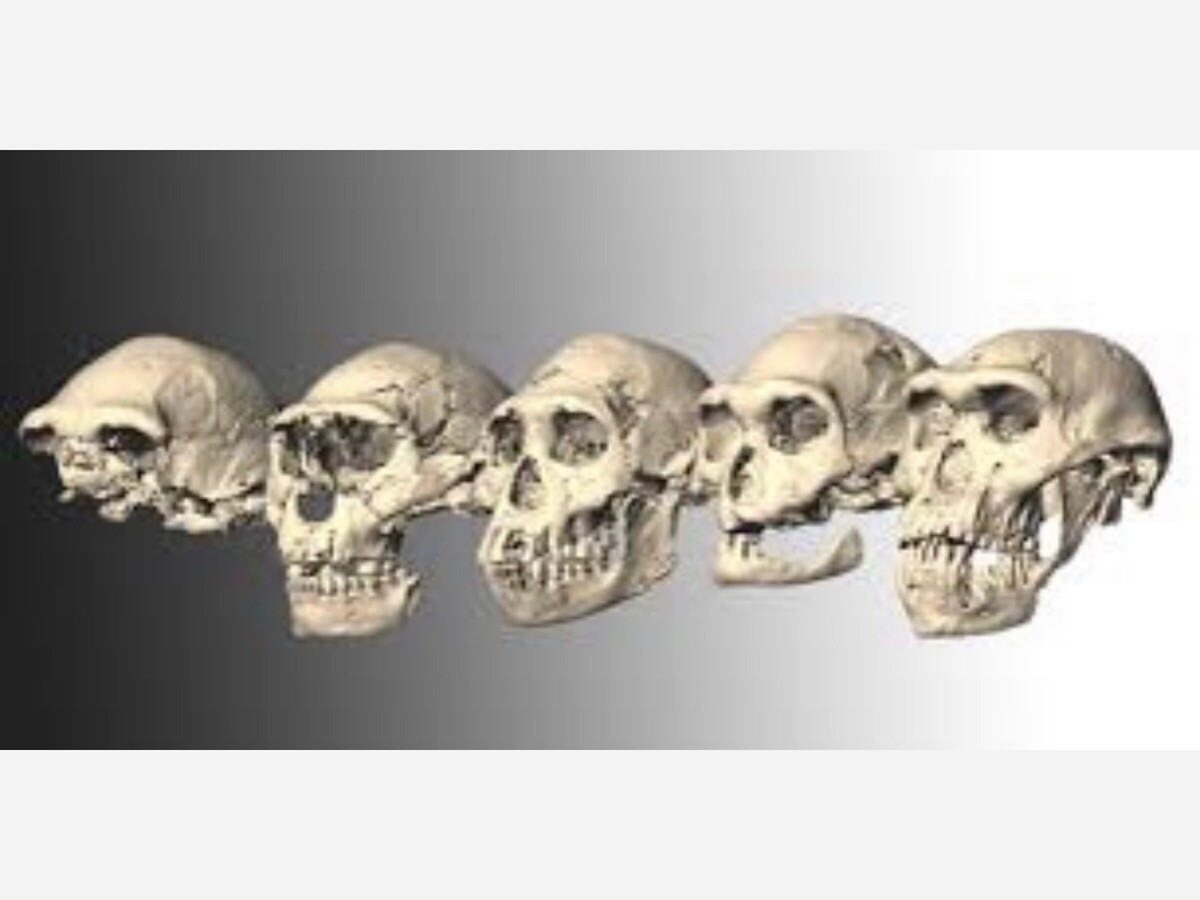
A new technology opens new answers and new insight into human survival and a near extinction event or period of human evolution. Science provides answers to human population evolution and a near extinction period for humanity. Nature took out 99% of the human population 800,000 years ago .
An unexplained gap in the African/Eurasian fossil record may now be explained thanks to a team of researchers from China, Italy and the United States. Using a novel method called FitCoal (fast infinitesimal time coalescent process), the researchers were able to accurately determine demographic inferences by using modern-day human genomic sequences from 3,154 individuals. These findings indicate that early human ancestors went through a prolonged, severe bottleneck in which approximately 1,280 breeding individuals were able to sustain a population for about 117,000 years. While this research has illuminated some aspects of early to middle Pleistocene ancestors, there are many more questions to be answered since uncovering this information.
A large amount of genomic sequences were analyzed in this study. However, “the fact that FitCoal can detect the ancient severe bottleneck with even a few sequences represents a breakthrough,” says senior author Yun-Xin Fu, a theoretical population geneticist at University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston.
During the Late Pleistocene, modern humans spread outside of the African continents and other human species like Neanderthals began to go extinct. The Australian continent and the Americas also saw humans for the first time and the climate was generally cold. This era is best known for its massive ice sheets and glaciers that shifted around the planet and shaped many of the landforms we see on Earth today.
In this study, released to Science.org the team used a new method called fast infinitesimal time coalescent process (FitCoal), as a way to determine ancient demographic inferences with modern-day human genomic sequences from 3,154 people.
“The fact that FitCoal can detect the ancient severe bottleneck with even a few sequences represents a breakthrough,” study co-author and University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston theoretical population geneticist Yun-Xin FU said in a statement.
FitCoal helped the team calculate what this ancient loss of life and genetic diversity looked like utilizing present-day genome sequences from 10 African and 40 non-African populations.
“The gap in the African and Eurasian fossil records can be explained by this bottleneck in the Early Stone Age chronologically,” study co-author and Sapienza University anthropologist Giorgio Manzi said in a statement. “It coincides with this proposed time period of significant loss of fossil evidence.”
Some of the potential reasons behind this population drop are mostly related to extremes in climate. Temperatures changed, severe droughts persisted, and food sources may have dwindled as animals like mammoths, mastodons, and giant sloths went extinct. According to the study, an estimated 65.85 percent of current genetic diversity may have been lost due to this bottleneck. The loss in genetic diversity prolonged a period of minimal numbers of humans who could successfully breed and was a major threat to the species.
However, this bottleneck also may have contributed to a speciation event, which happens when two or more species are created from a single lineage. During this speciation event, two ancestral chromosomes may have converged to form what is now chromosome 2 in modern humans. Chromosome 2 is the second largest human chromosome, and spans about 243 million building blocks of DNA base pairs. Understanding this split helped the team pinpoint what could be the last common ancestor for the Denisovans, Neanderthals, and Homo sapiens (modern humans).
“The novel finding opens a new field in human evolution because it evokes many questions, such as the places where these individuals lived, how they overcame the catastrophic climate changes, and whether natural selection during the bottleneck has accelerated the evolution of human brain,” co-author and East China Normal University evolutionary and functional genomics expert Yi-Hsuan PAN said in a statement.
In future studies, researchers could continue to find answers to how such a small population persisted in the face of climate adversity. It’s possible that learning to control fire and a climate that began to shift to be more hospitable to human life may have contributed to the rapid human population increase about 813,000 years ago.
Weird science but proof of a determination of our the human species to survive and adapt to an evolving environment and climate. From a low of 187,000 to 8 billion today.
Source: Science.org, ScienceDirect.com, EuerkaAlert.org,